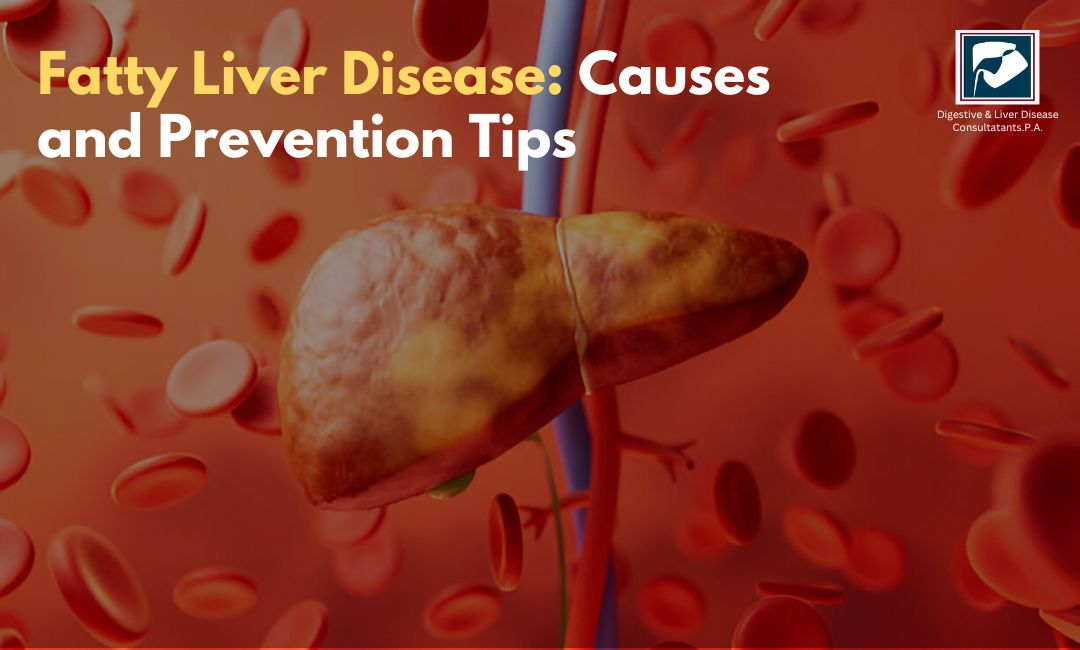
Fatty liver disease is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when too much fat builds up in the liver, potentially leading to serious health problems. Despite its prevalence, many people don’t fully understand what fatty liver disease is, its causes, or how to prevent it. This blog aims to provide clear and actionable information about this condition, empowering you to make informed decisions about your health.
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
The liver is a vital organ responsible for numerous essential functions, including filtering toxins, producing bile for digestion, and storing energy. When fat accumulates in the liver, it can interfere with these processes. Fatty liver disease typically falls into two main categories:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): This type occurs in people who drink little to no alcohol. It’s often linked to obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, and other metabolic conditions.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): This type results from excessive alcohol consumption, which damages the liver and promotes fat accumulation.
If left untreated, fatty liver disease can progress to more severe conditions, such as inflammation (steatohepatitis), scarring (fibrosis), or even liver failure.

Causes of Fatty Liver Disease
Understanding the causes of fatty liver disease is the first step in preventing it. Here are some common factors that contribute to its development:
Obesity: Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, is a significant risk factor for NAFLD.
Poor Diet: Consuming foods high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and processed ingredients can lead to fat buildup in the liver.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to weight gain and metabolic issues that can affect the liver.
Diabetes and Insulin Resistance: High blood sugar levels and insulin resistance are closely linked to fatty liver disease.
High Cholesterol or Triglycerides: Imbalances in blood lipids can promote fat accumulation in the liver.
Alcohol Consumption: In the case of AFLD, excessive drinking directly damages liver cells.
Other factors, such as certain medications, genetic predisposition, and rapid weight loss, can also contribute to fatty liver disease.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease is often called a “silent” condition because it may not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the disease progresses, you might experience:
- Fatigue
- Discomfort or pain in the upper right abdomen
- Unexplained weight loss
- Weakness
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), in severe cases
Because symptoms are not always apparent, regular check-ups and screenings are crucial, especially if you have risk factors for fatty liver disease.
Preventing Fatty Liver Disease
The good news is that fatty liver disease is often preventable, and even reversible, with lifestyle changes. Here are some practical steps you can take to protect your liver health:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is one of the most effective ways to reduce your risk of fatty liver disease. Aim for gradual, sustainable weight loss through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
2. Eat a Liver-Friendly Diet
Choose whole, nutrient-dense foods that support liver health. Focus on:
Fruits and Vegetables: These are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread provide essential nutrients and fiber.
Lean Proteins: Opt for chicken, fish, tofu, or legumes.
Healthy Fats: Include sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
Avoid sugary drinks, fried foods, and excessive salt, as these can worsen liver fat accumulation.
3. Stay Active
Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week to improve your overall health and reduce liver fat.
4. Limit Alcohol Consumption
If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation or avoid it altogether, especially if you’re at risk for fatty liver disease.
5. Manage Underlying Conditions
Control diabetes, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure through medication, lifestyle changes, or both. This can help prevent further damage to your liver.
6. Get Regular Check-Ups
Regular screenings can help detect liver problems early, even before symptoms appear.
When to See a Doctor
If you suspect you might have fatty liver disease or if you have risk factors like obesity or diabetes, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
At DLDC, our team of specialists is here to help you take control of your liver health. We offer comprehensive evaluations, personalized treatment plans, and support to guide you on your journey to better health.
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is a common but preventable condition that requires awareness and proactive management. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, eating a balanced diet, and staying active, you can significantly reduce your risk. Regular check-ups and timely medical care are also crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
If you’re concerned about fatty liver disease or need expert advice, don’t hesitate to reach out to DLDC.