Our state of the art offices offers the latest in technology and the convenience of full comprehensive gastrointestinal and liver disease care under one roof.
Convenient in office procedures such as Ultrasound, Capsule Endoscopy, Esophageal and Anorectal Manometry, Breath Testing & PH Studies are offered at our North Houston office and onsite lab services through Quest are provided in all three locations.
From consultative services and diagnostic procedures to more important endoscopic procedures, our physicians have achieved a seamless integration of services by providing them under one roof. Endoscopic procedural services include:
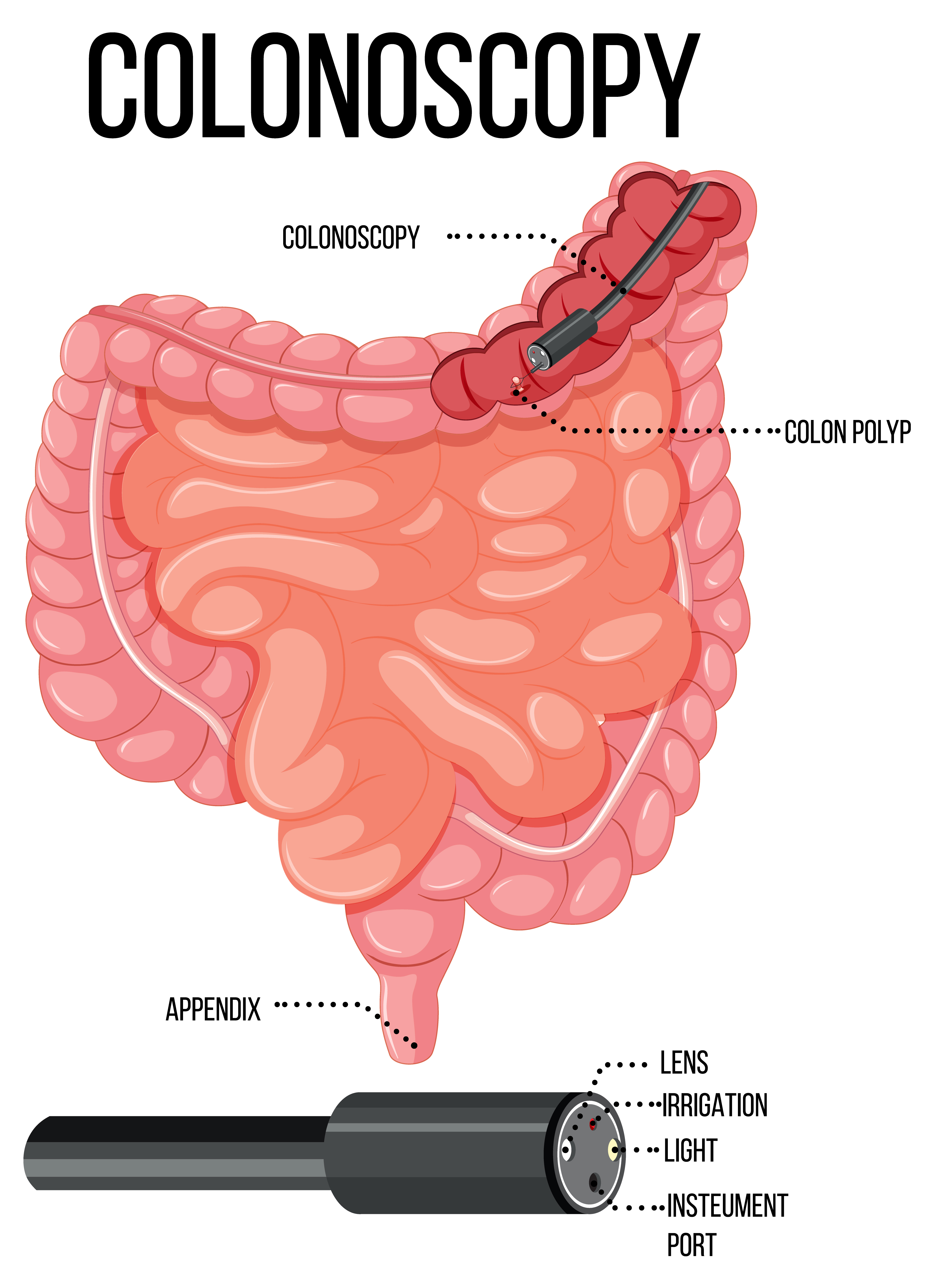
Learn about colonoscopy, a crucial procedure for detecting colorectal cancer and other digestive issues. Discover its benefits, preparation tips, and what to expect during and after the procedure.
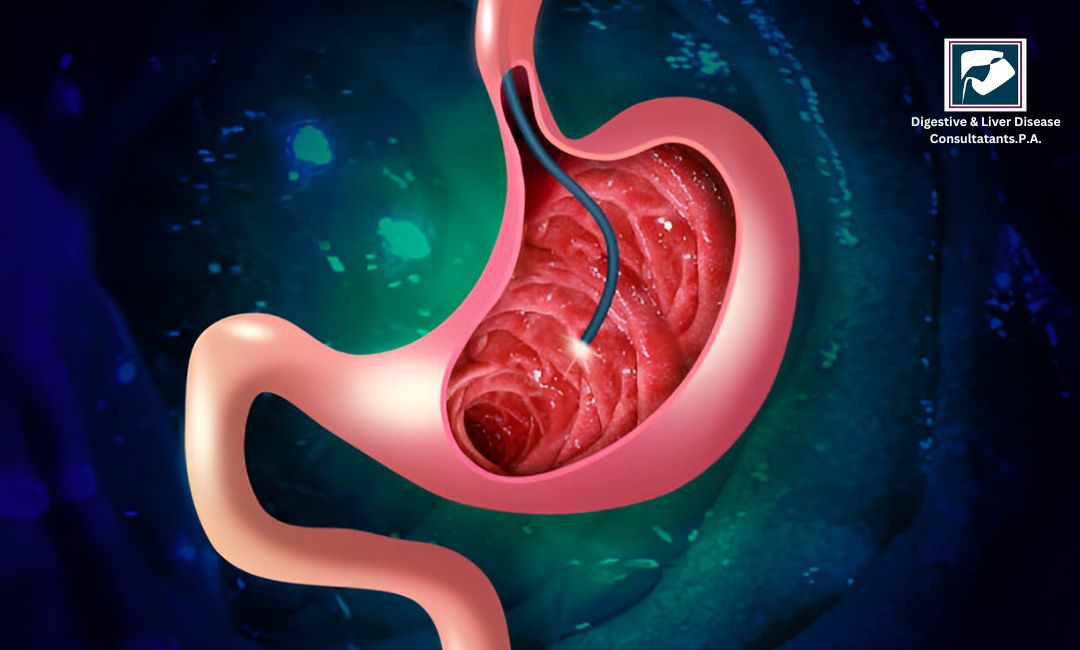
Learn about Upper Endoscopy (EGD), a procedure to diagnose digestive issues. Find out how it works, why it's needed, and schedule your appointment today.