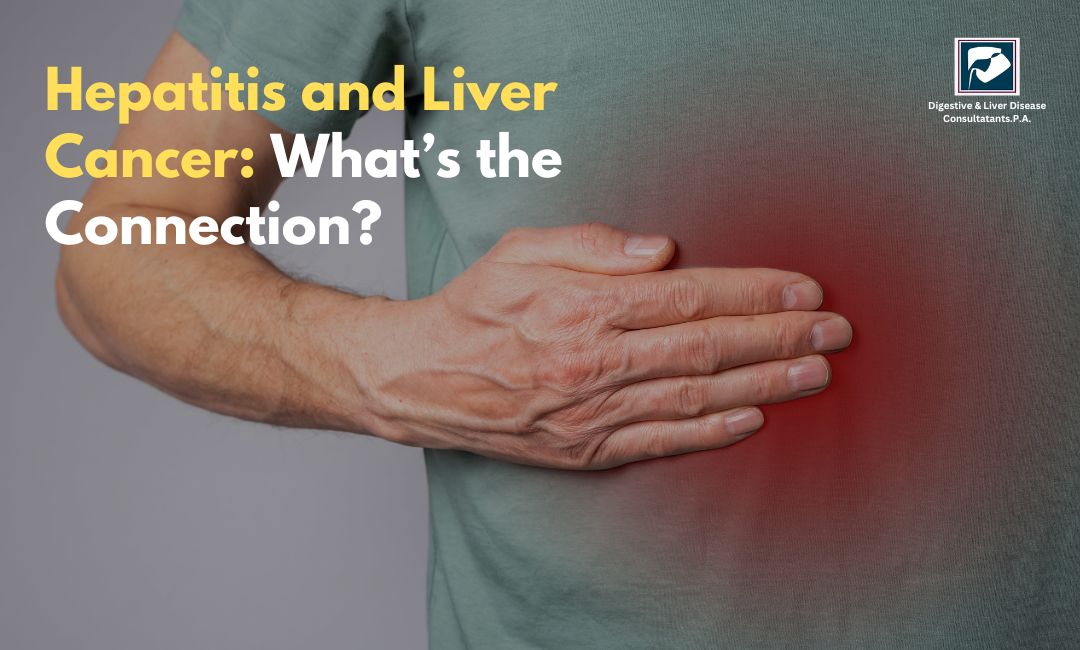
The liver is one of the most important organs in the body, responsible for filtering toxins, aiding digestion, and supporting metabolism. However, diseases like hepatitis can severely impact liver health and, in some cases, lead to liver cancer. Many people are unaware of the strong connection between hepatitis and liver cancer, but understanding this link can help with early detection and prevention.
In this blog, we’ll explore how hepatitis affects the liver, why it increases the risk of liver cancer, and what you can do to protect yourself.
What Is Hepatitis?
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, often caused by viral infections, excessive alcohol use, autoimmune diseases, or certain medications. The most common types of viral hepatitis are Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. Among these, Hepatitis B (HBV) and Hepatitis C (HCV) are the most concerning when it comes to liver cancer risk.
Types of Hepatitis:
Hepatitis A (HAV): A short-term infection caused by consuming contaminated food or water. It does not cause chronic liver disease.
Hepatitis B (HBV): A viral infection that spreads through blood, sexual contact, or from mother to baby at birth. It can become chronic and lead to serious liver damage.
Hepatitis C (HCV): Transmitted through infected blood, often due to sharing needles or unsterilized medical equipment. It frequently becomes chronic and is a leading cause of liver cancer.
Hepatitis D (HDV): A rare infection that only occurs in people already infected with Hepatitis B. It can worsen liver disease.
Hepatitis E (HEV): Typically spread through contaminated water, mainly in developing countries. It does not usually cause long-term liver problems.
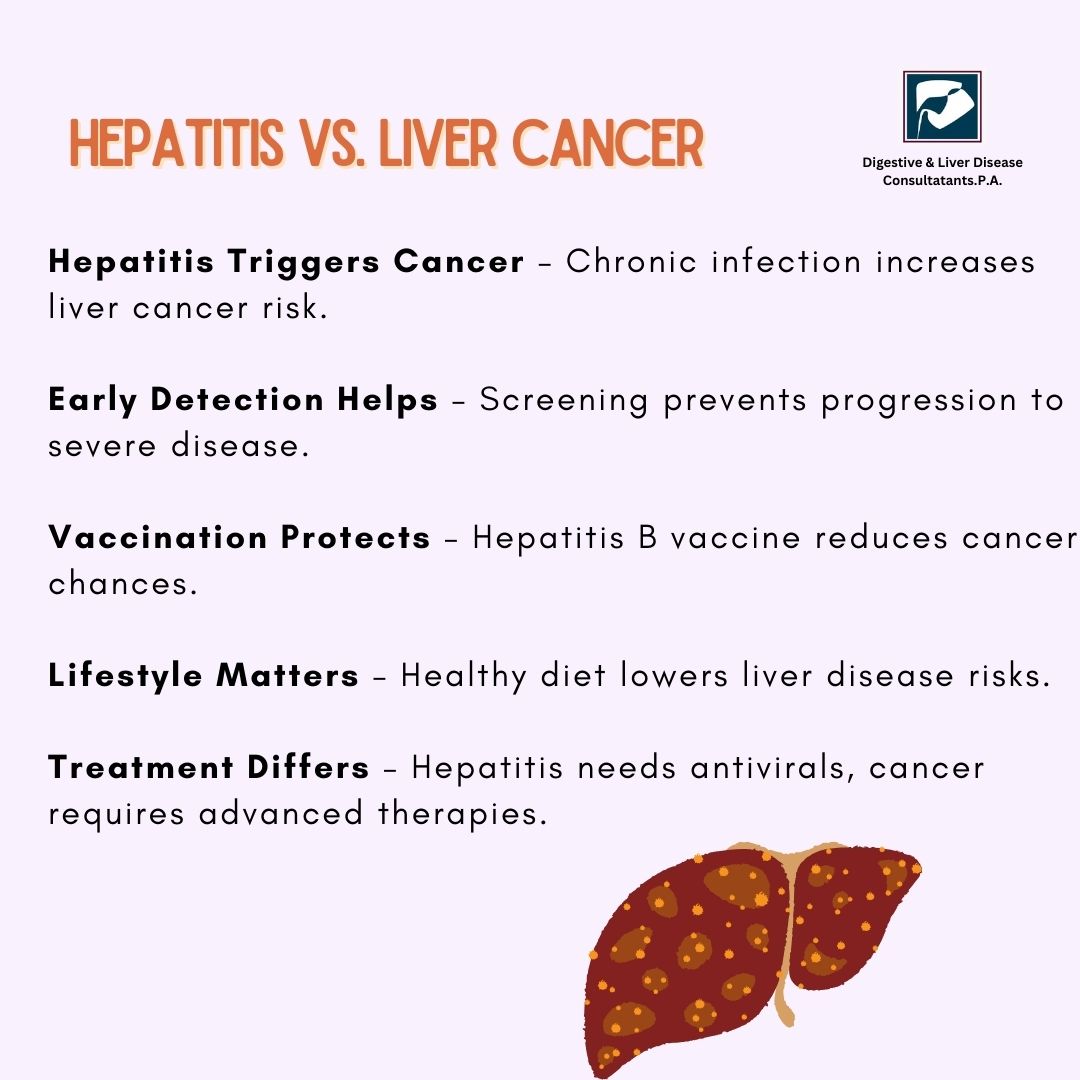
Among these, chronic Hepatitis B and C infections are the biggest threats when it comes to liver cancer.
How Does Hepatitis Lead to Liver Cancer?
Hepatitis B and C infections can cause chronic liver inflammation, which over time leads to scarring (cirrhosis) and increases the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of liver cancer.
Key Steps in Liver Cancer Development:
Chronic Inflammation: Long-term viral infection causes the immune system to continuously attack liver cells, leading to inflammation.
Liver Damage and Scarring: Persistent inflammation damages liver tissue, causing fibrosis (early scarring) and eventually cirrhosis (severe scarring).
Cell Mutations: As liver cells try to repair themselves, genetic mutations can occur, increasing the risk of cancerous growth.
Liver Cancer Formation: Over time, these cancerous cells can grow uncontrollably, leading to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
According to studies, about 80% of liver cancer cases worldwide are linked to chronic Hepatitis B or C infections.
Symptoms of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer symptoms may not appear in the early stages, making regular screenings essential for those at risk. However, as the disease progresses, symptoms may include:
- Persistent abdominal pain or discomfort
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue and weakness
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Swelling in the abdomen (ascites)
- Dark urine and pale stools
Since many of these symptoms can be linked to other conditions, it’s important to consult a liver specialist if you experience any of them.
Who Is at Risk for Liver Cancer?
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing liver cancer, including:
- Chronic Hepatitis B or C infection
- Cirrhosis (caused by hepatitis, alcohol abuse, or fatty liver disease)
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Obesity and fatty liver disease
- Diabetes
- Family history of liver cancer
- Exposure to aflatoxins (harmful substances found in contaminated food)
If you have any of these risk factors, it’s important to get regular liver screenings to detect problems early.
How to Prevent Hepatitis and Liver Cancer
1. Get Vaccinated
- The Hepatitis B vaccine is highly effective and recommended for all infants and high-risk adults.
- There is no vaccine for Hepatitis C, but early detection and treatment can prevent complications.
2. Get Tested and Treated
- Many people with Hepatitis B or C do not realize they are infected. A simple blood test can detect these infections.
- Antiviral treatments are available for both Hepatitis B and C, reducing the risk of liver damage and cancer.
3. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
- Limit alcohol intake to reduce liver damage.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly to maintain a healthy weight and prevent fatty liver disease.
4. Avoid Risky Behaviors
- Use protection during sex and avoid sharing needles to reduce the risk of hepatitis transmission.
- Be cautious with tattoos and piercings, ensuring proper sterilization of equipment.
Expert Care at Digestive & Liver Disease Consultants, P.A.
At Digestive & Liver Disease Consultants, P.A., we specialize in diagnosing and treating liver diseases, including hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Our team of experienced gastroenterologists and hepatologists provides personalized care to help patients manage their liver health effectively.
We offer:
- Comprehensive hepatitis screening and treatment
- Liver cancer surveillance and advanced diagnostic tests
- Personalized treatment plans for liver disease and cirrhosis
- State-of-the-art procedures and minimally invasive treatments
Your liver health matters. Early detection and treatment can save lives.
Conclusion
Hepatitis and liver cancer are closely connected, with chronic Hepatitis B and C being major risk factors. However, early diagnosis, vaccination, and a healthy lifestyle can help prevent serious complications.
If you have concerns about hepatitis, liver disease, or cancer risks, don’t wait. Schedule an appointment with Digestive & Liver Disease Consultants, P.A. today for expert care and guidance. Your liver health is in good hands!