When we think about mental health, the gut is probably not the first thing that comes to mind. However, an increasing amount of research reveals a fascinating connection between the two. Your gut, often referred to as the "second brain," plays a significant role in influencing your mood, mental clarity, and overall emotional well-being.
In this blog, we’ll explore the link between gut health and mental well-being, how the gut-brain connection works, and practical steps to maintain a healthy gut for a happier mind.
Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection
Your gut and brain are constantly communicating with each other through a network known as the gut-brain axis. This communication occurs via the vagus nerve, hormones, and chemical signals like neurotransmitters. Around 90% of the body's serotonin—a key neurotransmitter responsible for regulating mood—is produced in the gut.
The gut is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively called the gut microbiome. These microbes play a critical role in digestion, immunity, and the production of neurotransmitters. When the gut microbiome is in balance, it supports mental clarity and emotional resilience. On the other hand, an imbalanced gut can contribute to mental health challenges such as anxiety, depression, and brain fog.
How Gut Health Affects Mental Well-being
Production of Neurotransmitters
The gut produces neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which are essential for mood regulation. An unhealthy gut can disrupt the production of these chemicals, leading to mood imbalances.
Chronic Inflammation
Poor gut health can cause chronic inflammation in the body. This inflammation can reach the brain, potentially contributing to conditions like depression and anxiety.
Stress Response
An unhealthy gut can amplify the body’s stress response. Stress, in turn, disrupts gut health, creating a vicious cycle that can negatively impact mental well-being.
Immune System Regulation
The gut plays a central role in regulating the immune system. A healthy gut helps protect against harmful bacteria and reduces systemic inflammation, which can affect mood and brain health.
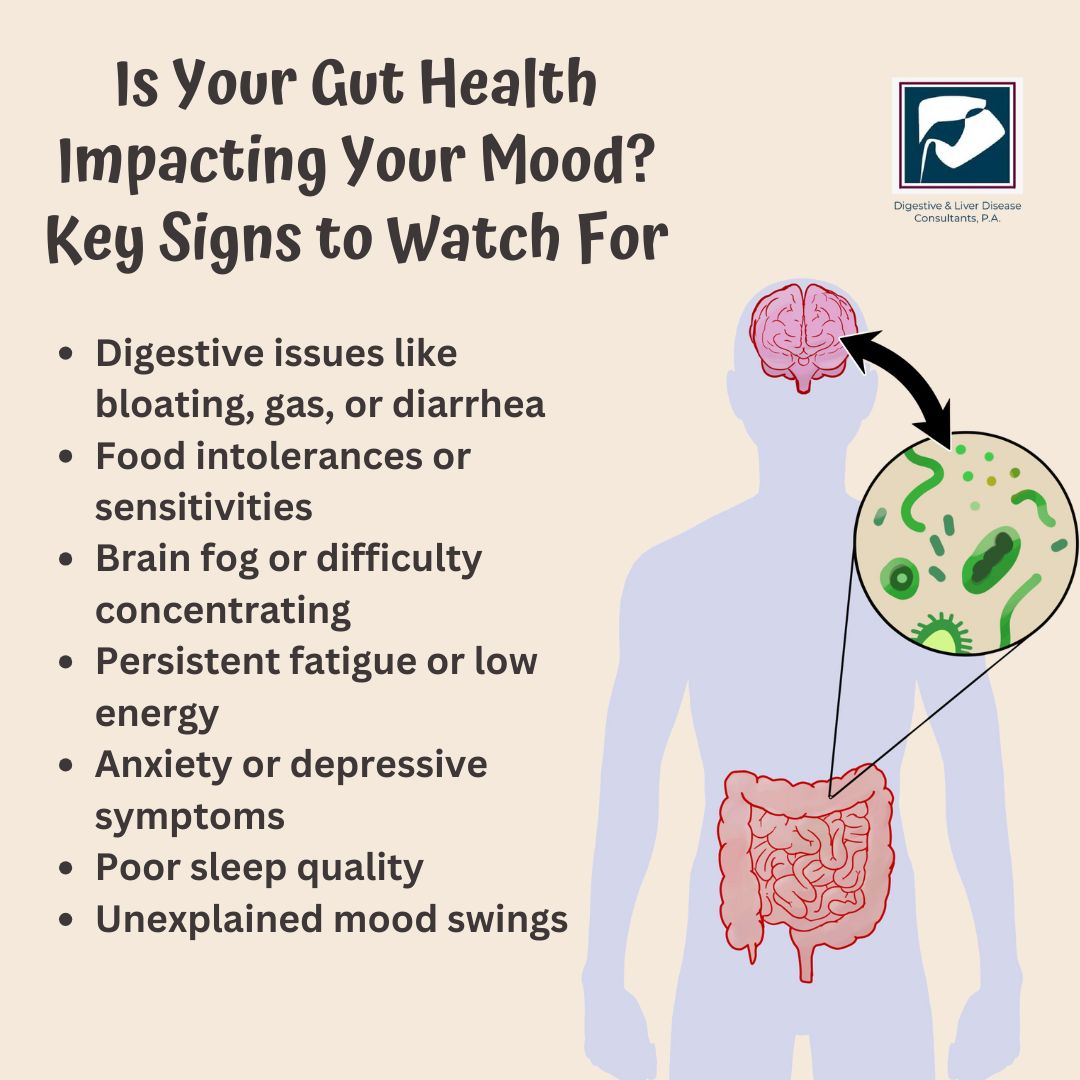
Signs Your Gut Health May Be Affecting Your Mind
If your gut health is out of balance, you may experience both physical and mental symptoms, such as:
- Digestive issues like bloating, gas, or diarrhea
- Food intolerances or sensitivities
- Brain fog or difficulty concentrating
- Persistent fatigue or low energy
- Anxiety or depressive symptoms
- Poor sleep quality
- Unexplained mood swings
Recognizing these signs early can help you take steps to restore balance and improve both your gut health and mental well-being.
Tips for a Healthy Gut and a Happy Mind
The good news is that nurturing your gut health can positively influence your mental well-being. Here are some practical tips:
Eat a Gut-Friendly Diet
Incorporate fibre-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut provide beneficial probiotics that support a healthy gut microbiome.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps maintain a healthy digestive system and supports overall gut function.
Manage Stress Levels
Chronic stress disrupts gut health. Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or spending time in nature.
Get Enough Sleep
Sleep is crucial for gut health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to allow your gut and brain to recover and repair.
Exercise Regularly
Physical activity not only benefits your body but also promotes a diverse and healthy gut microbiome.
Limit Processed Foods and Sugar
These can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and contribute to inflammation, which may affect mental health.
Consider Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics (found in supplements and fermented foods) introduce beneficial bacteria into your gut, while prebiotics (found in foods like garlic, onions, and bananas) feed the good bacteria already present.
Avoid Antibiotics Unless Necessary
While antibiotics are sometimes essential, overuse can harm the gut microbiome. Always consult your doctor before taking antibiotics.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
If you're experiencing gut-related symptoms such as bloating, diarrhea, or constipation, or if you're struggling with mental health issues like anxiety, depression, or mood swings, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider. By addressing both your physical and mental health, your doctor can help you create a treatment plan that supports overall well-being.
At DLDC (Digestive & Liver Disease Consultants P.A.), we specialize in helping patients achieve better gut health through personalized care. If you're suffering from gut health issues or mental well-being challenges, don’t hesitate to reach out to our expert team. We’ll work with you to improve your gut health and mental well-being, so you can live a happier, healthier life.
Conclusion: A Balanced Gut for a Balanced Mind
The connection between gut health and mental well-being is undeniable. By taking care of your gut, you’re not only improving digestion but also supporting a healthy mind and emotional resilience. Small, consistent lifestyle changes can lead to big improvements in how you feel, both physically and mentally.