Cirrhosis of the liver is a serious medical condition that affects many people, yet it’s often misunderstood. In simple terms, cirrhosis occurs when the liver becomes scarred and damaged over time. This scarring can prevent the liver from functioning properly, leading to significant health issues. Understanding the basics of cirrhosis, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower you to take steps toward better liver health.
What is Cirrhosis?
The liver is one of the most important organs in the body. It filters toxins, produces essential proteins, and aids in digestion. When the liver is repeatedly injured, whether due to alcohol use, infections, or other conditions, it tries to repair itself. This repair process can lead to scar tissue forming in the liver. Over time, excessive scarring can disrupt the liver's ability to function, resulting in cirrhosis.
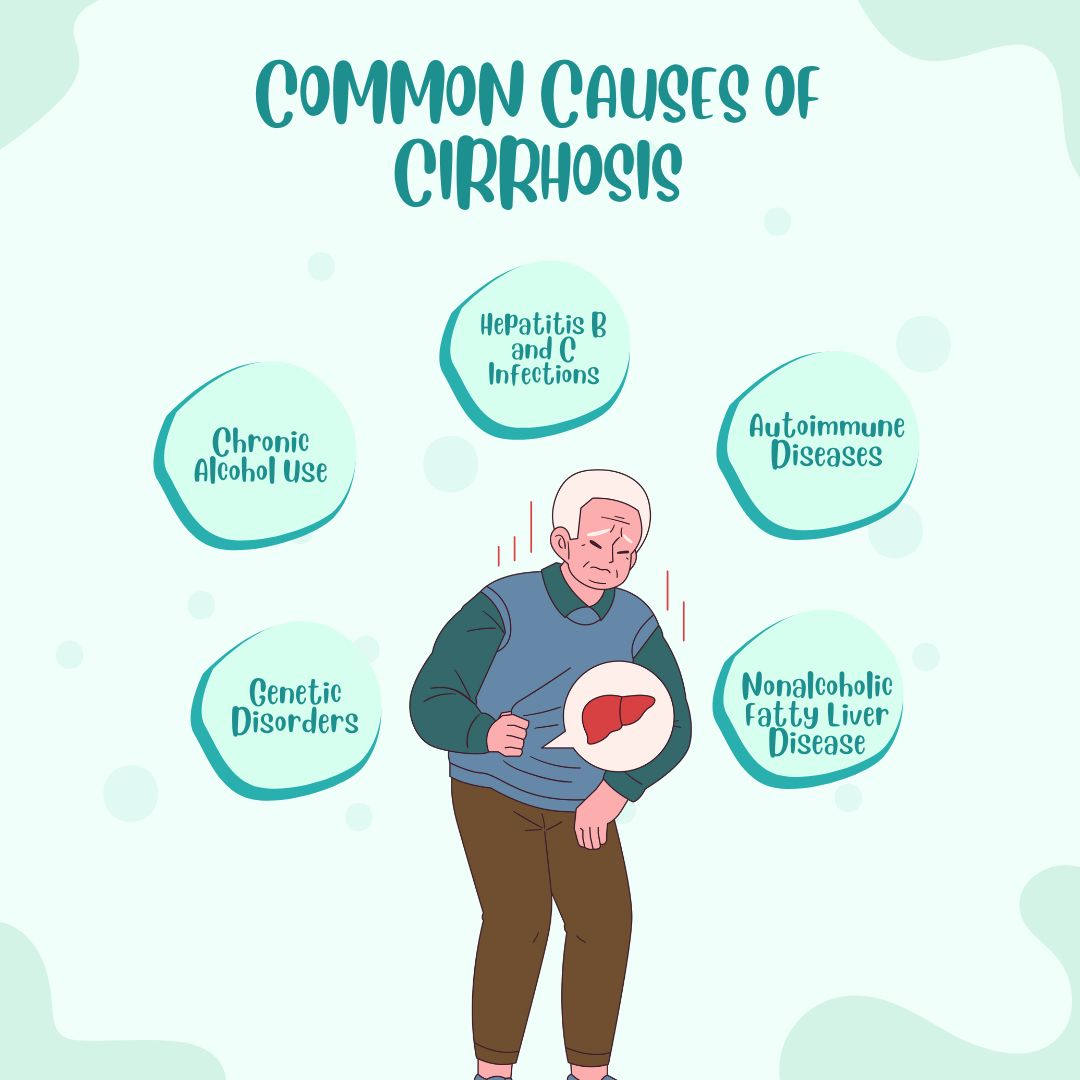
Common Causes of Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis develops for various reasons, but some of the most common causes include:
- Chronic Alcohol Use: Heavy drinking over many years can damage liver cells.
- Hepatitis B and C Infections: These viral infections can lead to long-term liver inflammation and scarring.
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Excess fat in the liver, often linked to obesity and diabetes, can cause damage.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions where the immune system attacks the liver can result in cirrhosis.
- Genetic Disorders: Diseases like hemochromatosis (iron buildup) or Wilson’s disease (copper buildup) can harm the liver.
Symptoms of Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis often develops silently, with no symptoms in its early stages. However, as the condition worsens, symptoms may appear, including:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Nausea
- Swelling in the legs or abdomen (edema and ascites)
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice)
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Confusion or difficulty thinking clearly (hepatic encephalopathy)
If you notice these symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis can help manage the disease effectively.
How is Cirrhosis Diagnosed?
Doctors use several methods to diagnose cirrhosis:
Medical History: Discussing your symptoms, lifestyle, and medical background.
Physical Exam: Checking for signs like jaundice, enlarged liver, or fluid buildup.
Blood Tests: Assessing liver function and identifying possible causes of liver damage.
Imaging Tests: Ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs provide detailed views of the liver.
Liver Biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of liver tissue is examined to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
While there’s no cure for cirrhosis, treatments can slow its progression, manage symptoms, and address underlying causes:
Lifestyle Changes: Quitting alcohol, maintaining a healthy weight, and following a liver-friendly diet can make a big difference.
Medications: Doctors may prescribe medications to treat the cause, such as antiviral drugs for hepatitis or diuretics to reduce swelling.
Monitoring and Care: Regular check-ups and blood tests help track liver function and manage complications.
Advanced Treatments: In severe cases, a liver transplant might be necessary.
Preventing Cirrhosis
You can take proactive steps to protect your liver and prevent cirrhosis:
- Limit alcohol intake or avoid it altogether.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis B.
- Practice safe habits to prevent hepatitis C, such as using clean needles and practising safe sex.
- Maintain a healthy weight and diet.
- Avoid unnecessary medications or toxins that may harm the liver.
- Living with Cirrhosis
Being diagnosed with cirrhosis can feel overwhelming, but many people manage the condition with proper medical care and lifestyle adjustments. Staying informed and proactive about your health is key.
When to See a Doctor
If you’re experiencing any symptoms of cirrhosis or are at risk due to alcohol use, hepatitis, or other factors, it’s important to consult a doctor. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve your quality of life.
At the Digestive and Liver Disease Clinic (DLDC) in the US, our team of experienced specialists is here to help. We provide comprehensive care, including advanced diagnostics and personalized treatment plans, to support your liver health.
Conclusion
Cirrhosis of the liver is a challenging condition, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help you take control of your health. If you’re concerned about your liver or experiencing symptoms, don’t wait—reach out for medical advice.
Contact DLDC today to schedule an appointment. Together, we’ll work toward a healthier future for you.